Essential Daily Tasks for Automotive Service Technicians: Complete Professional Guide
The foundation of automotive service excellence
Automotive service technicians perform numerous tasks throughout their workday, but two core responsibilities stand above all others in terms of importance and frequency: diagnostic troubleshooting and preventive maintenance services. These pair activities form the backbone of professional automotive service and direct impact customer satisfaction, vehicle safety, and business success.
Understand which tasks take priority help both aspire technicians and industry professionals focus their skills development efforts efficaciously. The automotive service industry demand technical expertise across multiple systems, but master these fundamental task pairs create a solid foundation for career advancement.
Primary task pair: diagnostic analysis and problem resolution
Diagnostic troubleshooting represent the about intellectually demanding and technically critical aspect of automotive service work. Modern vehicles contain sophisticated electronic systems, complex mechanical components, and integrate computer networks that require systematic analysis when problems arise.
Effective diagnostic work begin with gather detailed information from customers about their vehicle’s symptoms. Technicians must listen cautiously to descriptions of unusual sounds, performance issues, warning lights, or operational concerns. This initial consultation phase frequently provides crucial clues that guide subsequent testing procedures.
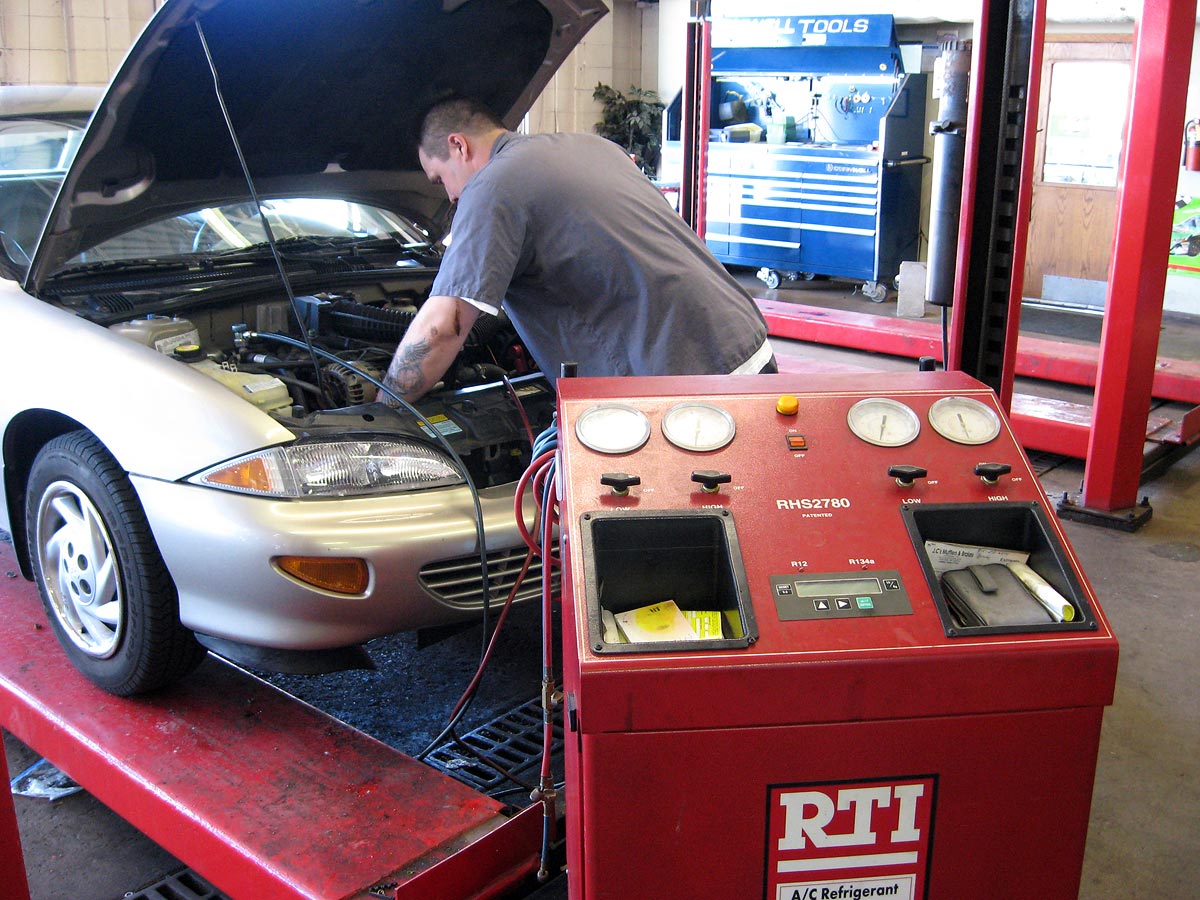
The diagnostic process involve multiple steps that technicians repeat throughout their daily workflow. First, visual inspections help identify obvious problems like fluid leaks, wear components, or damaged parts. Future, technicians connect specialized diagnostic equipment to vehicle computer systems to retrieve error codes and performance data.
Modern diagnostic tools provide unprecedented access to vehicle system information. Scan tools can monitor real time engine parameters, transmission behavior, brake system performance, and emission control functions. Nonetheless, interpret this data require extensive technical knowledge and practical experience.
Problem resolution follow successful diagnosis and involve select appropriate repair procedures, order necessary parts, and execute repairs accord to manufacturer specifications. Technicians must document their work exhaustively and verify that repairs address the original customer concerns wholly.
Secondary task pair: preventive maintenance and system inspections
Preventive maintenance services constitute the second well-nigh important task category for automotive service technicians. These routine procedures help prevent major mechanical failures, extend vehicle lifespan, and maintain optimal performance levels.
Oil changes represent the nearly common preventive maintenance service, but comprehensive maintenance involve lots more than fluid replacement. Technicians inspect multiple vehicle systems during routine service appointments, check tire condition, brake wear, battery performance, and fluid levels throughout the vehicle.
Systematic inspection procedures help technicians identify potential problems before they cause vehicle breakdowns or safety hazards. For example, detect brake pad wear during routine maintenance allow customers to schedule brake service at their convenience kinda than experience brake failure circumstantially.
Filter replacements, fluid exchanges, and component lubrication form essential parts of preventive maintenance protocols. Air filters, fuel filters, cabin air filters, and oil filters require regular replacement to maintain proper system function. Transmission fluid, brake fluid, coolant, and power steering fluid need periodic inspection and replacement base on manufacturer recommendations.
Tire rotation, wheel alignment checks, and suspension system inspections help ensure safe vehicle handling and prevent premature tire wear. These services require specialized equipment and precise measurement techniques that technicians must master through training and practice.
Integration of core tasks in daily workflow
Successful automotive service technicians seamlessly integrate diagnostic work and preventive maintenance throughout their daily schedules. A typical workday might begin with diagnose a customer’s engine performance complaint, follow by perform routine maintenance on several vehicles, so return to complete the morning’s diagnostic repair.
Time management skills become crucial when balance these different task types. Diagnostic work oftentimes require extended periods of focused analysis, while routine maintenance follow more predictable time schedules. Technicians must estimate job completion times accurately to maintain efficient shop operations.
Customer communication play a vital role in both task categories. During diagnostic work, technicians must explain complex technical problems in terms customers can understand. For preventive maintenance, technicians need to educate customers about service benefits and recommend maintenance schedules.
Documentation requirements apply to both diagnostic and maintenance work. Technicians must record diagnostic test results, repair procedures, parts use, and service recommendations. This documentation protects both customers and service facilities while provide valuable information for future service needs.
Technical skills’ development for core tasks
Master diagnostic troubleshooting require continuous learning as automotive technology evolve quickly. Technicians must stay current with new diagnostic equipment, update repair procedures, and emerge vehicle technologies. Hybrid and electric vehicles present new diagnostic challenges that require specialized training and equipment.
Electrical system knowledge become progressively important as vehicles incorporate more electronic components. Understand circuit operation, component testing procedures, and wiring diagram interpretation help technicians diagnose complex electrical problems expeditiously.
Mechanical aptitude remain fundamental for both diagnostic and maintenance work. Technicians must understand how automotive systems interact, recognize normal versus abnormal component wear patterns, and select appropriate tools for specific repair procedures.
Computer literacy skills support modern diagnostic work as scan tools become more sophisticated and repair information moves to digital formats. Technicians access technical service bulletins, wiring diagrams, and repair procedures through computer base information systems.
Safety considerations in daily operations
Both diagnostic work and preventive maintenance involve significant safety considerations that technicians must address systematically. Vehicle lift procedures, electrical system safety, fluid handling protocols, and personal protective equipment usage protect technicians from workplace injuries.
Proper lifting techniques prevent back injuries when handle heavy components during diagnostic work or maintenance procedures. Vehicle support safety ensure that cars remain stable during undercarriage inspections and repairs.
Chemical safety protocols protect technicians from exposure to automotive fluids, clean solvents, and other hazardous materials normally use in service operations. Understand material safety data sheets and use appropriate protective equipment reduce health risks importantly.
Electrical safety become critical when diagnose modern vehicle systems that operate at various voltage levels. High voltage hybrid and electric vehicle systems require specialized safety training and equipment to prevent serious injuries.
Quality control and customer satisfaction
Quality control measures ensure that both diagnostic and maintenance work meet professional standards systematically. Technicians must verify repair effectiveness through road testing, system operation checks, and follow-up inspections.
Customer satisfaction depend intemperately on accurate problem diagnosis and thorough repair completion. Misdiagnosis lead to unnecessary repairs, customer frustration, and potential warranty claim that damage shop reputation.
Preventive maintenance quality immediately impacts customer vehicle reliability and safety. Incomplete or incorrect maintenance procedures can cause premature component failures or create safety hazards that expose service facilities to liability concerns.
Communication skills help technicians explain repair necessity, maintenance benefits, and service value to customers efficaciously. Build customer trust through honest communication and quality work create long term business relationships.
Technology integration in modern service operations
Contemporary automotive service rely intemperately on technology integration for both diagnostic and maintenance tasks. Shop management software track customer service history, schedules appointments, and manage parts inventory expeditiously.
Digital inspection systems allow technicians to document vehicle conditions with photographs and detailed notes that customers can review remotely. These systems improve communication transparency and help customers understand recommend service needs.
Remote diagnostic capabilities enable technicians to access vehicle data and manufacturer technical support resources promptly. Cloud base information systems provide instant access to repair procedures, technical service bulletins, and diagnostic troubleshooting guides.
Mobile device integration allow technicians to access repair information, order parts, and communicate with customers direct from their work locations. This technology streamline workflow and reduce time spend move between work areas and office locations.
Career development through core task mastery
Master diagnostic troubleshooting and preventive maintenance create advancement opportunities within the automotive service industry. Senior technician positions, shop foreman roles, and service advisor positions all require expertise in these fundamental areas.
Specialization opportunities emerge from strong diagnostic skills, include transmission repair, electrical system diagnosis, or hybrid vehicle service. These specialized fields oftentimes offer higher compensation and increase job security.
Certification programs through organizations like the national institute for automotive service excellence recognize technician competency in specific areas. These credentials demonstrate professional expertise to employers and customers.

Source: iumch.org
Continue education requirements help technicians maintain current knowledge as automotive technology advances. Manufacturer training programs, community college courses, and industry seminars provide ongoing learn opportunities.
Industry trends affect core tasks
Electric vehicle adoption change both diagnostic and maintenance requirements importantly. Electric powertrains require different diagnostic approaches, specialized tools, and modify maintenance schedules compare to traditional internal combustion engines.
Advanced driver assistance systems create new diagnostic challenges as vehicles incorporate radar sensors, cameras, and complex software systems. Technicians must understand these systems to diagnose problems and perform calibration procedures aright.
Connected vehicle technology enable remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance scheduling. These capabilities change how technicians interact with vehicle systems and communicate with customers about service needs.
Environmental regulations influence both diagnostic procedures and maintenance practices. Emission system diagnosis become more complex, and waste disposal requirements affect shop operations importantly.
Professional excellence in automotive service
Excellence in automotive service stem from consistent execution of diagnostic troubleshooting and preventive maintenance tasks. These core responsibilities require technical competency, attention to detail, and commitment to customer satisfaction.
Successful technicians develop systematic approaches to both diagnostic work and routine maintenance that ensure consistent results. Create personal checklists, follow manufacturer procedures, and document work exhaustively support professional service delivery.

Source: poshmark.com
Build expertise in these fundamental areas provide a solid foundation for career advancement and professional recognition. The automotive service industry rewards technicians who demonstrate competency, reliability, and commitment to quality workmanship.
The combination of diagnostic skills and maintenance expertise position automotive service technicians as essential professionals in keep vehicles safe, reliable, and efficient. These core competencies remain relevant disregarding of how automotive technology continue to evolve.
MORE FROM promospotlight.com