Automotive Service Facility Hazard Classification: Understanding Safety Requirements and Compliance Standards
Understand hazard classifications for automotive service facilities
Automotive service and repair facilities fall under specific hazard categories that reflect the unique risks associate with vehicle maintenance, repair operations, and the handling of various automotive fluids and materials. These facilities are typically classify as
Moderate hazard occupancies
Under fire protection codes and safety regulations, though specific classifications can vary base on the scope of operations and materials present.
The classification system take into account multiple factors include the types of chemicals store and use, the presence of flammable liquids, electrical systems, and the general fire load of the facility. Understand these classifications is crucial for facility owners, managers, and safety professionals to ensure proper compliance with building codes, fire protection requirements, and occupational safety standards.
Primary hazard category classification
Most automotive service facilities are classified under Group s 1 occupancy Accord to the international building code (iIBC) which cover moderate hazard storage and service facilities. This classification specifically apapplieso facilities engage in service motor vehicles and include provisions for the storage of automotive fluids, parts, and equipment typically find in these environments.
The moderate hazard classification acknowledge that while automotive service facilities do not present the extreme risks associate with heavy manufacturing or chemical processing plants, they do involve importantly more hazardous materials and processes than typical office or retail environments. This middle ground classification require specific safety measures without the well-nigh stringent requirements reserve for high hazard facilities.
Factors influence classification
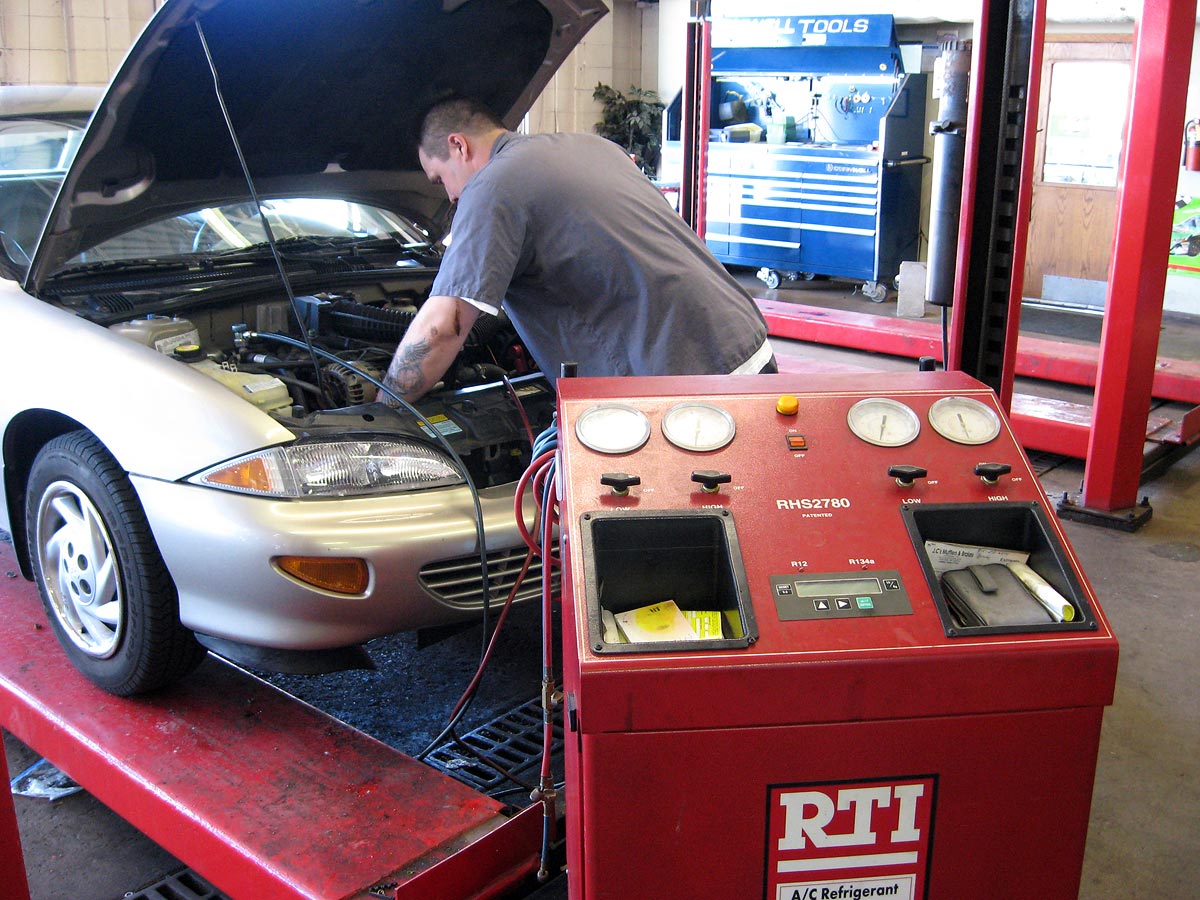
Several key factors determine the exact hazard classification for automotive service facilities. The quantity and types of flammable liquids store on site play a major role, include gasoline, diesel fuel, motor oil, transmission fluid, brake fluid, and various cleaning solvents. Facilities that store larger quantities of these materials may face additional requirements or subclassifications.
The presence of spray paint operations, welding activities, and tire services can elevate certain areas of the facility to higher hazard classifications. Paint booths, for example, are typically classify as high hazard areas require specialized ventilation, fire suppression systems, and electrical equipment rate for hazardous locations.
Fire protection requirements
Automotive service facilities must comply with specific fire protection requirements base on their hazard classification. These typically include automatic sprinkler systems design for ordinary hazard occupancies, though areas with higher concentrations of flammable liquids may require foam suppression systems or other specialized fire protection measures.
Portable fire extinguishers must be strategically place throughout the facility, with class b extinguishers require for flammable liquid fires and class c extinguishers for electrical fires. The spacing and capacity of these extinguishers must meet national fire protection association (nNFPA)standards for automotive service facilities.
Emergency exits and egress paths must be clear mark and maintain, with adequate width and number of exits base on occupancy load calculations. Exit routes can not pass through areas of higher hazard classification, such as paint booths or chemical storage areas.
Ventilation and air quality management
Proper ventilation systems are critical in automotive service facilities to manage vehicle exhaust, chemical vapors, and airborne contaminants. General ventilation requirements typically call for a minimum number of air changes per hour, while specific areas like service pits, paint booths, and parts cleaning stations require dedicated exhaust systems.
Vehicle exhaust removal systems must be installed at service bay locations where engines aoperatedate indoors. These systems should capture exhaust at the source and vent it safely outside the building, prevent the accumulation of carbon monoxide and other harmful gases in the work environment.
Chemical storage and handling requirements
The storage and handling of automotive chemicals and fluids are subject to strict regulations base on the facility’s hazard classification. Flammable liquids must be store in approve containers and cabinets, with quantity limitations base on the specific classification of each chemical and the overall facility design.
Use oil storage require secondary containment systems to prevent environmental contamination, while waste materials must be right segregate and store accord to their hazard classifications. Many automotive facilities maintain separate storage areas for different types of hazardous materials to minimize compatibility issues and reduce overall risk.

Source: iaeimagazine.org
Spill containment and cleanup procedures must be established and communicate to all employees. Emergency spill kits should be pronto available, and staff should be train in proper cleanup procedures for different types of automotive fluids and chemicals.
Regulatory compliance considerations
Automotive service facilities must comply with multiple regulatory frameworks, include occupational safety and health administration (oOSHA)standards, environmental protection agency ( (aEPA)gulations, and local fire codes. The hazard classification help determine which specific regulations apply and the extent of compliance requirements.
Regular inspections by local fire departments, environmental agencies, and safety officials are common for facilities in this hazard category. Maintain proper documentation of safety procedures, employee training, and equipment maintenance is essential for demonstrating ongoing compliance.
Electrical system requirements
Electrical installations in automotive service facilities must meet specific standards base on the presence of flammable vapors and liquids. While most areas of a typical service facility do not require explosion proof electrical equipment, certain locations such as service pits, areas near fuel storage, and spray paint operations may require special electrical classifications.
Ground fault circuit interrupters (gFCS) )e typically require for electrical outlets in areas where water and automotive fluids may be present. Proper grounding of all electrical equipment and systems is essential to prevent static electricity buildup that could ignite flammable vapors.
Emergency lighting and exit signs must be connecteto back upup power sources to ensure safe evacuation during power outages. These systems shoube testedest regularly and maintain accord to manufacturer specifications and local code requirements.
Equipment and machinery safety
Automotive service equipment such as lifts, air compressors, and diagnostic equipment must meet safety standards appropriate for the facility’s hazard classification. Regular inspection and maintenance of this equipment is required to ensure safe operation and prevent accidents that could escalate due to the presence of flammable materials.

Source: emo trans global.com
Vehicle lifts require particular attention as they present both mechanical hazards and potential ignition sources if not right maintain. Hydraulic fluid leaks from lifts can create slip hazards and potential fire risks if the fluid contacts hot surfaces or ignition sources.
Employee training and safety protocols
Staff training requirements for automotive service facilities reflect the moderate hazard classification and include education on fire prevention, chemical handling, emergency procedures, and proper use of personal protective equipment. Employees must understand the specific risks associate with their work environment and know how to respond befittingly to various emergency situations.
Regular safety meetings and refresher training help maintain awareness of hazards and ensure that safety procedures remain current with change regulations and best practices. Documentation of training activities is important for regulatory compliance and liability protection.
Personal protective equipment requirements may include safety glasses, gloves resistant to automotive chemicals, non-slip footwear, and respiratory protection when work with certain materials or in unwell ventilate areas.
Emergency response planning
Emergency response plans for automotive service facilities must address the specific hazards present in the moderate hazard classification. These plans should cover fire response procedures, chemical spill cleanup, medical emergencies, and evacuation procedures tailor to the facility layout and operations.
Coordination with local emergency responders is important to ensure they understand the specific hazards present at the facility and can respond befittingly to different types of emergencies. Pre incident planning with fire departments can help identify potential challenges and develop effective response strategies.
Insurance and liability considerations
The hazard classification of automotive service facilities direct impact insurance requirements and premiums. Insurance providers assess risk base on the types of operations conduct, materials store, and safety measures implement. Facilities that exceed minimum safety requirements may qualify for reduced premiums or other incentives.
Liability considerations include potential environmental contamination, fire damage to adjacent properties, and worker injury claims. Proper classification and compliance with safety requirements help minimize these risks and provide legal protection in the event of incidents.
Regular safety audits and risk assessments can help identify potential problems before they result in accidents or regulatory violations. These proactive measures demonstrate due diligence and can be valuable in insurance claims or legal proceedings.
Future trends and evolving standards
The automotive service industry continues to evolve with new vehicle technologies, include electric and hybrid vehicles, which present different hazards and may influence future classification standards. High voltage electrical systems in electric vehicles require specialized training and safety procedures that may affect facility classifications.
Environmental regulations continue to become more stringent, specially regard the handling and disposal of automotive fluids and materials. Facilities must stay current with change requirements to maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
Advances in fire suppression technology, ventilation systems, and safety equipment provide opportunities for automotive service facilities to enhance safety while potentially reduce compliance costs. Stay inform about new technologies and best practices help facility managers make informed decisions about safety investments.
Understand the hazard classification system for automotive service facilities is essential for ensure workplace safety, regulatory compliance, and business continuity. The moderate hazard classification reflects the unique combination of risks present in these facilities while provide a framework for implement appropriate safety measures. Regular review of safety procedures, ongoing employee training, and stay current with evolve regulations help maintain a safe and compliant operation that protect workers, customers, and the surround community.
MORE FROM promospotlight.com