Automotive Engineering: Complete Guide to Career Responsibilities and Impact
Understand automotive engineering
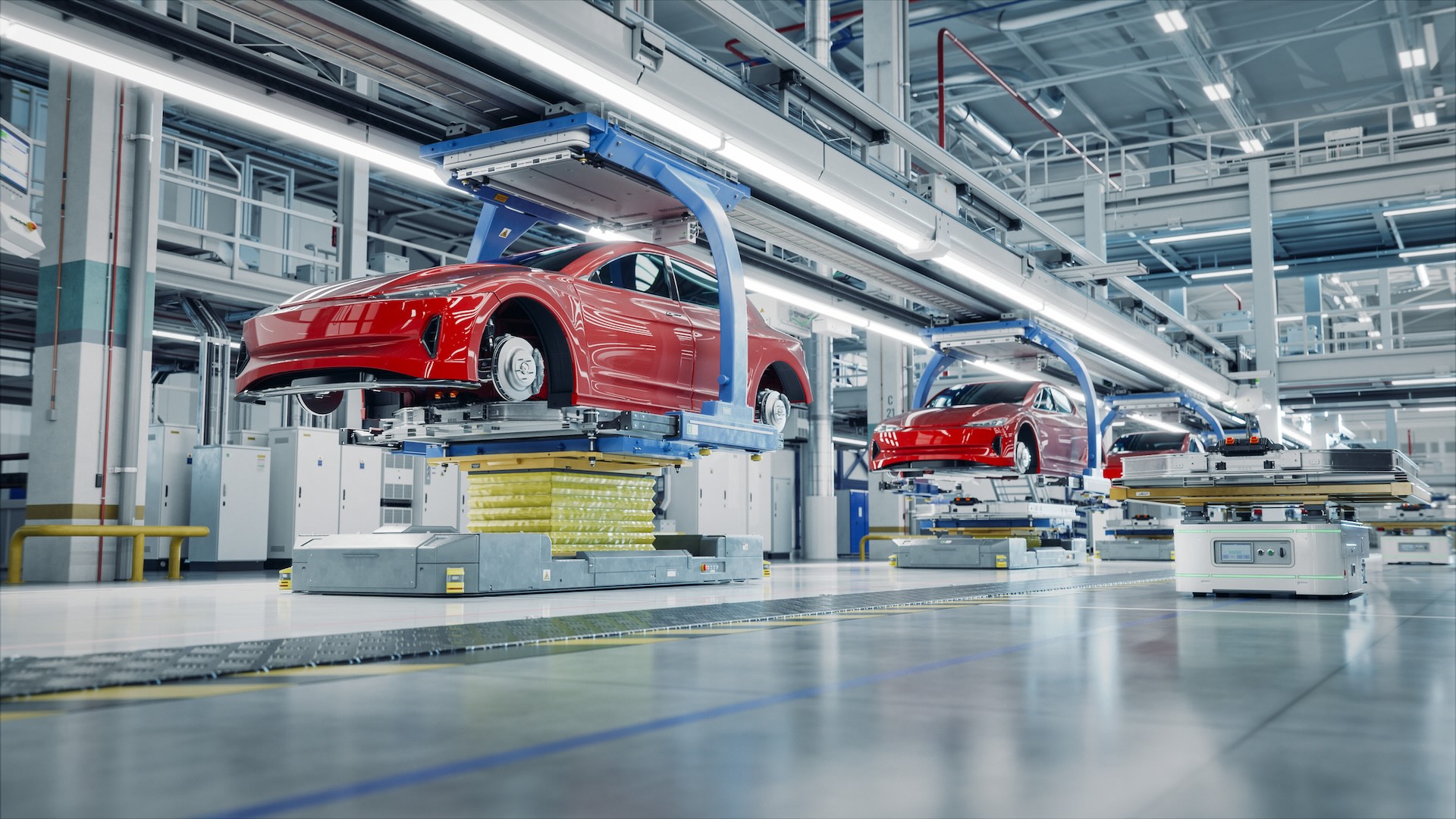
Automotive engineering represent one of the virtually dynamic and impactful fields in modern engineering. These specialized professionals design, develop, manufacture, and test vehicles and their components, play a crucial role in shape how we move through the world. The field combine mechanical engineering principles with cutting edge technology to create safer, more efficient, and progressively intelligent transportation solutions.
Automotive engineers work across multiple disciplines, integrate knowledge from mechanical, electrical, software, and materials engineering. Their work direct influence vehicle performance, safety, fuel efficiency, and environmental impact. As the automotive industry undergo rapid transformation with electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and smart connectivity, these engineers are at the forefront of revolutionary change.
Core responsibilities of automotive engineers
Vehicle design and development
Automotive engineers begin their work in the conceptual phase, where they translate ideas into functional vehicle designs. They create detailed specifications for engines, transmissions, chassis, suspension systems, and body structures. This process involve extensive computer aid design (cad )work, where engineers model components and systems before physical prototypes are build.
The design process require balance multiple factors include performance requirements, safety standards, manufacturing costs, and regulatory compliance. Engineers must consider how different systems interact with each other and ensure that the final product meet both consumer expectations and industry standards.
Testing and validation
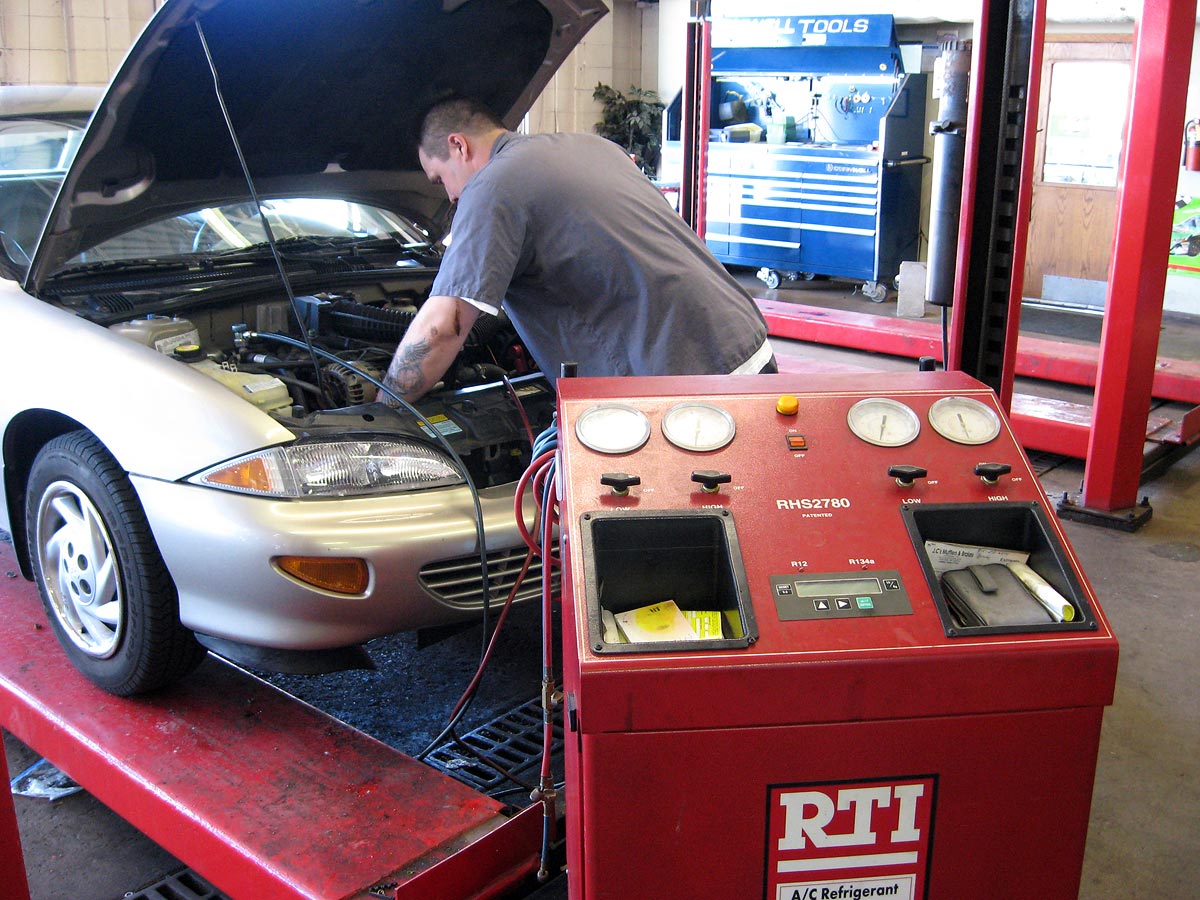
Rigorous testing form a cornerstone of automotive engineering work. Engineers conduct various tests include crash simulations, durability assessments, performance evaluations, and emissions testing. They use sophisticated testing equipment and computer simulations to validate designs before vehicles reach production.
Testing encompass both component level and system level validation. Engineers test individual parts like brake systems, engines, and electronic components so evaluate how these systems work unitedly in complete vehicles. This comprehensive approach ensure reliability and safety across all operating conditions.
Manufacturing process development
Automotive engineers play a vital role in develop efficient manufacturing processes. They work intimately with production teams to design assembly lines, specify manufacturing equipment, and establish quality control procedures. This involves optimize production workflows to minimize costs while maintain high quality standards.
Manufacturing engineering require deep understanding of materials science, production techniques, and automation systems. Engineers must ensure that designs can be manufacture systematically and cost efficaciously at scale, oftentimes involve thousands of vehicles per day.
Specialized areas within automotive engineering
Powertrain engineering
Powertrain engineers focus on the systems that generate and deliver power to move vehicles. This includes internal combustion engines, electric motors, transmissions, and hybrid systems. They work to optimize fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and improve performance characteristics.
With the shift toward electrification, powertrain engineers are progressively involved in battery technology, electric motor design, and energy management systems. They must understand both traditional mechanical systems and advanced electrical technologies.
Safety systems engineering
Safety engineers develop and implement systems design to protect vehicle occupants and other road users. They work on passive safety features like airbags, seatbelts, and crumple zones, arsenic advantageously as active safety systems include anti lock brakes, stability control, and collision avoidance technologies.
Modern safety engineering progressively involves advanced driver assistance systems( Adas) that use sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence to prevent accidents. These engineers must understand both mechanical systems and sophisticated software algorithms.
Electronics and software engineering
Contemporary vehicles contain numerous electronic systems and millions of lines of software code. Automotive electronics engineers develop infotainment systems, engine control units, communication networks, and autonomous driving technologies.
This specialization require expertise in embed systems, real time programming, and automotive communication protocols. Engineers must ensure that electronic systems operate faithfully in harsh automotive environments while meet strict safety and performance requirements.
Daily work environment and activities
Collaborative project work
Automotive engineers typically work in multidisciplinary teams that include other engineers, designers, technicians, and project managers. They participate in regular design reviews, where teams evaluate progress and make decisions about design directions.
Collaboration extend beyond internal teams to include suppliers, regulatory agencies, and sometimes customers. Engineers must communicate complex technical concepts to diverse audiences and incorporate feedback from multiple stakeholders.
Computer base design and analysis
Much of an automotive engineer’s work involve computer base tools for design, simulation, and analysis. They use cad software to create detailed 3d models, finite element analysis programs to predict structural behavior, and computational fluid dynamics tools to optimize aerodynamics.
These digital tools allow engineers to explore design alternatives rapidly and cost efficaciously before build physical prototypes. Advanced simulation capabilities enable testing of scenarios that would be difficult or dangerous to replicate in real world conditions.
Hands on testing and prototyping
Despite extensive computer modeling, automotive engineers regularly work with physical prototypes and test vehicles. They conduct laboratory tests, participate in vehicle testing on test tracks, and analyze real world performance data.
This hands on work provide crucial validation of computer models and reveal issues that might not be apparent in simulations. Engineers oftentimes spend time in testing facilities, manufacturing plants, and field locations gather data and observe system behavior.
Educational requirements and career path
Academic foundation
Most automotive engineers hold bachelor’s degrees in mechanical engineering, automotive engineering, or related fields. The curriculum typically includes mathematics, physics, materials science, thermodynamics, and mechanical design principles.
Many engineers pursue advanced degrees to specialize in particular areas or to advance into research and development roles. Graduate programs oft focus on specific technologies like electric powertrains, autonomous systems, or advanced materials.

Source: engineeringfactsz.com
Professional development
The automotive industry evolve quickly, require engineers to unendingly update their skills and knowledge. Professional development include attend conferences, participate in training programs, and stay current with emerge technologies.
Many engineers pursue professional engineering licenses and certifications in specialized areas. Industry organizations provide resources for ongoing education and network opportunities.
Industry impact and future directions
Environmental sustainability
Automotive engineers play a crucial role in address environmental challenges through the development of cleaner, more efficient vehicles. They work on electric and hybrid powertrains, lightweight materials, and improve aerodynamics to reduce environmental impact.
Sustainability considerations influence every aspect of automotive engineering, from material selection to end of life recallability. Engineers must balance performance requirements with environmental responsibility.
Autonomous vehicle development
The development of self drive vehicles represent one of the virtually significant challenges in automotive engineering. Engineers work on sensor systems, artificial intelligence algorithms, and fail-safe mechanisms that enable vehicles to operate safely without human intervention.
This emerges field require expertise in traditional automotive engineering combine with knowledge of computer science, artificial intelligence, and human factors engineering.
Connected vehicle technologies
Modern vehicles progressively communicate with infrastructure, other vehicles, and cloud base services. Automotive engineers develop the hardware and software systems that enable these connections while ensure cybersecurity and privacy protection.
Connected vehicle technologies promise to improve traffic efficiency, enhance safety, and enable new mobility services. Engineers must consider both technical capabilities and user experience in develop these systems.
Career opportunities and specializations
Industry sectors
Automotive engineers work in various industry sectors include traditional automakers, electric vehicle startups, autonomous vehicle companies, and automotive suppliers. Each sector offer different opportunities and challenges.

Source: newkidscar.com
The expand definition of mobility create opportunities in ride-share companies, logistics firms, and technology companies develop automotive solutions. Engineers can apply their skills across a broader range of organizations than always ahead.
Geographic opportunities
The automotive industry operates globally, provide opportunities for engineers to work in different countries and cultures. Major automotive centers exist inNorth Americaa,Europee,Asiaa, and progressively in emerge markets.
International experience can be valuable for engineers seek to understand global markets and regulatory environments. Many automotive companies offer international assignments and cross-cultural collaboration opportunities.
Automotive engineering offer a rewarding career path for individuals passionate about technology, innovation, and improve how people move through the world. The field combine technical challenges with practical applications that instantly impact millions of people every day. As the automotive industry will continue to will evolve with new technologies and will change consumer expectations, automotive engineers will remain essential to drive progress and innovation in transportation.
MORE FROM promospotlight.com