Automotive Air Conditioning Technician Licensing: Complete Guide to Required Certifications
Essential licensing requirements for automotive ac technicians
Automotive air conditioning service and repair technicians must obtain specific licenses and certifications to lawfully work with vehicle cool systems. The near critical requirement is EPA section 609 certification, which authorize technicians to handle refrigerants use in mobile air conditioning systems.
The environmental protection agency mandates this certification under the clean air act to prevent harmful refrigerant emissions. Without proper licensing, technicians can not lawfully purchase, handle, or dispose of automotive refrigerants, make certification essential for anyone work in this field.
EPA section 609 certification requirements
EPA section 609 certification specifically cover mobile air conditioning (mac )systems in cars, trucks, and other vehicles. This certification differ from stationary hvHVACertifications and focus on automotive specific requirements.
To obtain section 609 certification, technicians must pass an EPA approve test cover refrigerant recovery, recycling, and proper handling procedures. The exam include questions about ozone depletion, global warming potential, and environmental regulations affect automotive refrigerants.
Testing organizations approve by the EPA include ASE (automotive service excellence ) macs ( (bile air conditioning society ),)nd other recognize bodies. Many technical schools and automotive training centers offer preparation courses and testing services.
Certification process and testing
The section 609 test typically consist of 25 multiple choice questions cover core competencies. Candidates must achieve a pass score of 84 % or higher. The exam cover topics include refrigerant identification, recovery equipment operation, leak detection methods, and proper disposal procedures.
Test preparation materials are available through EPA approve organizations and cover essential knowledge areas such as refrigerant properties, system components, service procedures, and environmental regulations. Many candidates find hands-on training valuable for understanding practical applications.
State and local licensing requirements
Beyond EPA certification, some states require additional licensing for automotive technicians work on air conditioning systems. These requirements vary importantly by location and may include general automotive technician licenses or specialized HVAC credentials.
California, for example, have specific requirements for technicians work with refrigerants, while other states may require general automotive service licenses. Some municipalities besides impose local licensing requirements for businesses offer automotive ac services.
Technicians should research their specific state and local requirements, as non-compliance can result in fines, business closure, or legal liability. State licensing boards typically provide current information about requirements and application procedures.
Professional certification programs
ASE certification in heating and air conditioning (a7 )provide additional credibility and demonstrate advanced competency in automotive climate control systems. While not lawfully require, this certification enenhancesrofessional standing and employment opportunities.
The a7 certification cover comprehensive knowledge of automotive HVAC systems, include electrical diagnosis, component replacement, and performance testing. This voluntary certification requires pass a detailed examination and demonstrate relevant work experience.
Refrigerant handling and recovery equipment
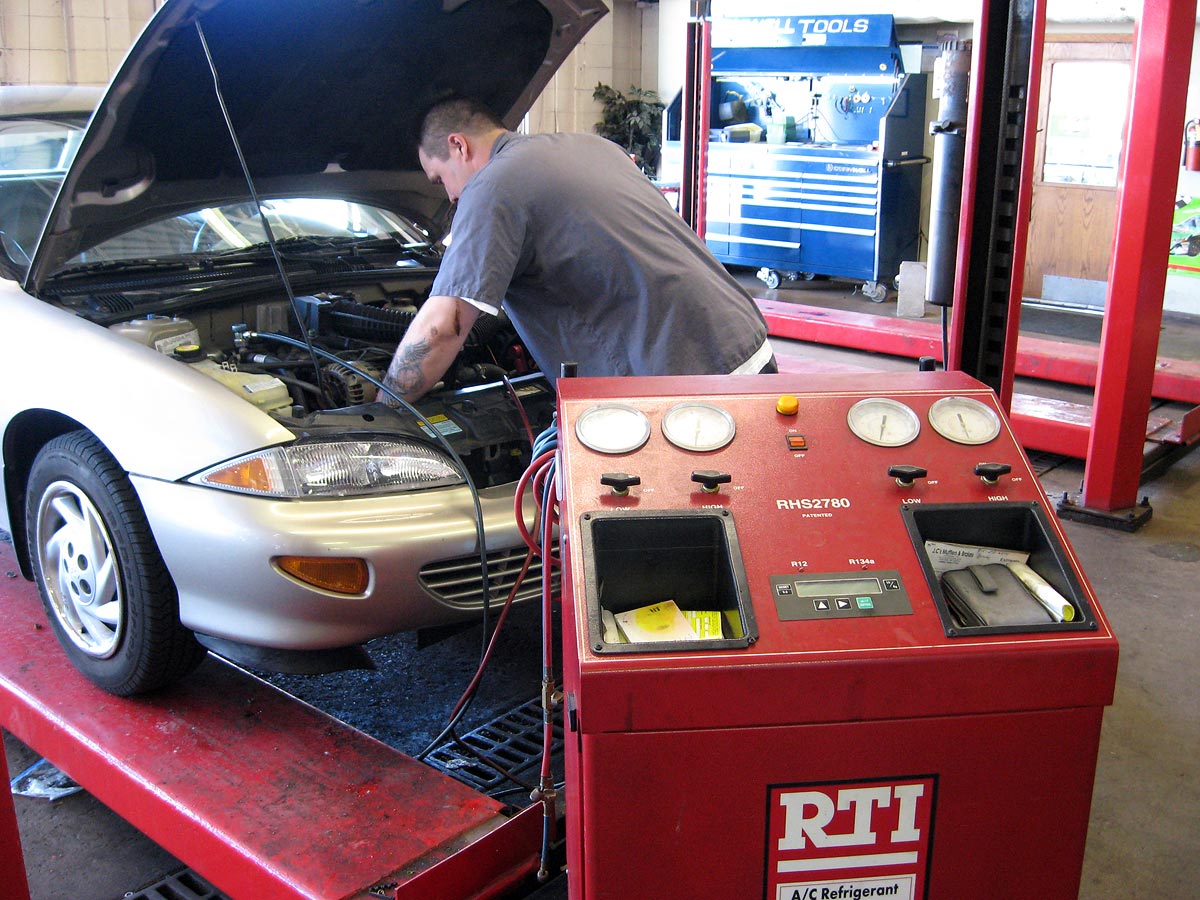
Licensed technicians must use EPA approve recovery and recycling equipment when service automotive ac systems. This equipment must meet specific standards and undergo regular certification to ensure proper operation.

Source: numerade.com
Recovery machines must be certified yearly or after every 1,000 pounds of refrigerant process, whichever come 1st. Technicians are responsible for maintain equipment certification and keep detailed records of refrigerant handling activities.
Proper equipment operation include connect recovery machines aright, monitor system pressures, and ensure complete refrigerant removal before system service. Technicians must besides verify equipment functionality and calibration regularly.
Record keeping and documentation
EPA regulations require detailed record keeping for all refrigerant transactions and service activities. Technicians must document refrigerant purchases, system services, recovery amounts, and disposal activities.
Records must include customer information, vehicle details, refrigerant types and quantities, service dates, and technician certification numbers. These records must be maintained for at least three years and make available foEPApa inspection upon request.
Types of automotive refrigerants and regulations
Modern vehicles use various refrigerant types, each with specific handling requirements and regulations. R 134a remain common in many vehicles, while newer systems progressively use r 1234yf, which have lower global warming potential.
Each refrigerant type require specific knowledge and handle procedures. R 1234yf, for instance, is gently flammable and require additional safety precautions during service. Technicians must understand these differences and follow appropriate procedures for each refrigerant type.
Older vehicles may stock still contain r 12 (cCFC12 ) which is no retentive produce and require special handling procedures. Technicians encounter r 12 systems must follow strict recovery and disposal protocols to prevent environmental damage.
Safety considerations and best practices
Automotive ac technicians must follow strict safety protocols when work with refrigerants and pressurized systems. Personal protective equipment, include safety glasses and gloves, is essential for prevent injury from refrigerant exposure.
Proper ventilation is crucial when work with refrigerants, as some types can displace oxygen in confine spaces. Technicians should besides be aware of refrigerant flammability characteristics and take appropriate fire prevention measures.

Source: popsautoelectric.com
Training and education requirements
Many automotive technicians receive ac system training through formal education programs at technical schools or community colleges. These programs typically cover system theory, component identification, diagnostic procedures, and hands on service techniques.
Manufacturer specific training is oftentimes valuable, as different vehicle brands may use unique system designs or service procedures. Many automotive manufacturers offer training programs for technicians work on their vehicles.
Continue education is important for stay current with evolve technology and change regulations. New refrigerant types, system designs, and environmental regulations require ongoing learning and skill development.
Apprenticeship and on the job training
Many technicians develop ac service skills through apprenticeship programs or on the job training with experienced professionals. This practical experience complement formal education and provide real world problem solve skills.
Experienced technicians can provide valuable mentorship in areas such as diagnostic techniques, customer service, and business practices. This combination of formal training and practical experience create intimately rounded professionals.
Business licensing and insurance considerations
Automotive service businesses offer ac repair must oftentimes obtain business licenses and maintain appropriate insurance coverage. General business licenses, automotive service permits, and environmental compliance certifications may be required.
Liability insurance is specially important for businesses handle refrigerants, as environmental damage claims can be substantial. Professional liability coverage protects against claims relate to improper service or equipment damage.
Some insurance providers offer specialized coverage for automotive service businesses, include protection against refrigerant relate environmental claims and equipment coverage for expensive recovery machines.
Compliance and inspection requirements
EPA enforcement include periodic inspections of automotive service facilities to verify compliance with refrigerant handling regulations. Inspectors review technician certifications, equipment certifications, and service records.
Violations can result in significant fines and legal action. Common violations include uncertified technicians, improper equipment use, inadequate record keeping, and refrigerant venting to the atmosphere.
Career advancement and specialization
Licensed automotive ac technicians can pursue various career paths, include specialization in specific vehicle types, hybrid and electric vehicle systems, or commercial vehicle applications. Each specialization may require additional training and certification.
Management positions in automotive service facilities oftentimes prefer candidates with strong technical credentials, include EPA certification and professional certifications. Business ownership is another career path for experienced technicians.
The growth complexity of automotive climate control systems create opportunities for technicians with advanced diagnostic skills and electronic system knowledge. Continuous learning and skill development are essential for career advancement.
Industry trends and future requirements
Environmental regulations continue to evolve, with increase emphasis on refrigerants with lower global warming potential. Technicians must stay informed about regulatory changes and new refrigerant introductions.
Electric and hybrid vehicles present new challenges and opportunities for ac technicians, as these systems oft use different components and operating principles. Additional training may be required for service these advanced systems.
Technology integration in automotive systems require technicians to develop computer diagnostic skills and understand complex electronic controls. This technological evolution create demand for extremely skilled, decent license professionals.
Maintain certification and continuing education
EPA section 609 certification does not expire, but technicians must stay current with regulatory changes and industry developments. Many professionals pursue additional certifications and training to maintain their competitive edge.
Professional organizations such as macs and ASE offer continue education opportunities, technical updates, and network opportunities for automotive ac technicians. These resources help professionals stay current with industry changes.
Regular equipment training and manufacturer update ensure technicians can efficaciously service newer vehicle models and emerge technologies. This ongoing education investment pay dividends in career advancement and earn potential.
MORE FROM promospotlight.com